Routine cytogenetic analysis
Routine cytogenetic analysis by the Cytogenetics Core requires metaphase slides prepared by the core. Typically, 20 to 30 metaphases are analyzed primarily using GTL banding (G banding) unless other staining methods are required.
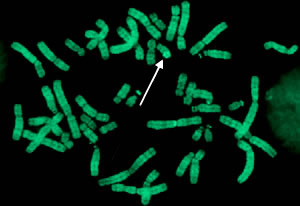
Q-banded metaphase from a healthy male with the Y chromosome (arrow)
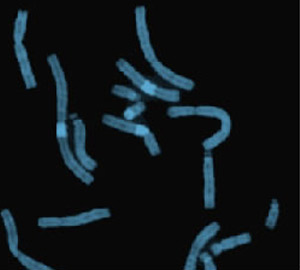
Representative partial metaphase illustrating distamycin-A/DAPI staining
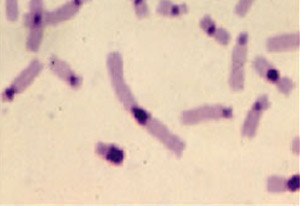
Representative partial metaphase illustrating C banding
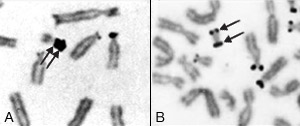
Representative nucleolar organizing region-banded partial metaphases illustrating double satellites (A) and an isodicentric chromosome with satellites at both ends (B)
Details
- GTL-banding (G banding). This Giemsa-staining method is used to identify individual chromosomes and their structural anomalies given the resulting banding pattern. G banding is widely used in clinical practice because it produces distinct permanent bands that allow for the identification of all human chromosomes and accurate characterization of numeric and structural anomalies.
- QFQ-banding (Q banding). This fluorescent staining method, which uses quinacrine, is used to identify individual chromosomes and their structural anomalies, given the resulting banding pattern. The characteristic banding pattern can be used to identify each chromosome accurately.
- Distamycin-A/DAPI staining. This staining method identifies heterochromatic regions found on chromosomes 1, 9, 15, 16 and Y.
- CBL-banding (C banding). This staining method is used to analyze normal and abnormal structural variations in chromosomes by locating centromeric and Yq constitutive heterochromatin.
- AgNOR staining for satellite regions.Silver staining of nuclear organizer regions (AgNOR) is used to locate nucleolar organizer regions on chromosomes. It's useful for studies of chromosomes with double satellites, chromosome polymorphisms and structural abnormalities involving satellite regions.
- Nonbanding. This chromosome banding technique uses nucleoprotein stains such as Geimsa to produce uniformly stained chromosomes. Typically, 20 metaphases are stained by nonbanding and analyzed for minor anomalies, such as chromatid breaks and gaps; major anomalies, such as acentric fragments and dicentric chromosomes; and radial configurations, such as triradials, quadriradials and complex radial formations.